A Detailed Overview Of AWS SES and Monitoring - Part 2
In our interconnected digital world, managing email efficiently and securely is a critical aspect of business operations. This post delves into a sophisticated setup using Amazon Web Services (AWS) that ensures your organization's email communication remains robust and responsive. Specifically, we will explore using AWS Simple Email Service (SES) in conjunction with Simple Notification Service (SNS) and AWS Lambda to handle email bounces and complaints effectively.
Understanding the Components
Before diving into the setup, let's understand the components involved:
- AWS SES: An email service that enables you to send and receive emails securely.
- AWS SNS: A flexible, fully managed pub/sub messaging and mobile notifications service for coordinating the delivery of messages to subscribing endpoints and clients.
- AWS Lambda: A serverless compute service that runs your code in response to events and automatically manages the underlying compute resources.
The Need for Handling Bounces and Complaints
Managing bounces and complaints efficiently is crucial for maintaining your organization’s email sender reputation. High rates of bounces or complaints can affect your ability to deliver emails and could lead to being blacklisted by email providers.
Step-by-Step Setup
Step 1: Configuring SES
First, configure your AWS SES to handle outgoing emails. This involves:
- Setting up verified email identities (email addresses or domains from which you'll send emails).
- Creating configuration sets in SES to specify how emails should be handled and tracked.
Step 2: Integrating SNS for Notifications
The next step is to set up AWS SNS to receive notifications from SES. This is crucial for real-time alerts on email bounces or complaints:
- Create an SNS topic that SES will publish to when specified events (like bounces or complaints) occur.
- Configure your SES configuration set to send notifications to the created SNS topic.
{
"Version": "2008-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ses.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "SNS:Publish",
"Resource": "arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:<account number>:SES-tracking",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"AWS:SourceAccount": "<account number>"
},
"StringLike": {
"AWS:SourceArn": "arn:aws:ses:*"
}
}
}
]
}
Step 3: Using AWS Lambda for Automated Responses
With SNS in place, integrate AWS Lambda to automate responses based on the notifications:
- Create a Lambda function that will be triggered by notifications from the SNS topic.
- Program the Lambda function to execute actions like logging the incident, updating databases, or even triggering remedial workflows.
import boto3, os, json
from botocore.exceptions import ClientError
# Set the global variables
fromEmail= str(os.getenv('from_email','from email address'))
ccEmail = str(os.getenv('cc_email','cc email address'))
toEmail = str(os.getenv('cc_email','to email address'))
awsRegion = str(os.getenv('aws_region','us-east-1'))
# The character encoding for the email.
CHARSET = "UTF-8"
# Create a new SES resource and specify a region.
sesClient = boto3.client('ses',region_name=awsRegion)
def sendSESAlertEmail(eventData):
message = eventData['Records'][0]['Sns']['Message']
print("message = "+message)
bouceComplaintMsg = json.loads(message)
print("bouceComplaintMsg == "+str(bouceComplaintMsg))
json_formatted_str_text = pp_json(message )
if "bounce" in bouceComplaintMsg:
print("Email is bounce")
# The email body for recipients with non-HTML email clients.
BODY_TEXT = "SES: Bounce email notification" +"\r\n"+json_formatted_str_text
bounceEmailAddress = bouceComplaintMsg['bounce']['bouncedRecipients'][0]['emailAddress']
bounceReason = bouceComplaintMsg['bounce']['bouncedRecipients'][0]['diagnosticCode']
print("bounceEmailAddress == "+bounceEmailAddress)
print("bounceReason == "+bounceReason)
subject = "SES Alert: Email to "+bounceEmailAddress+" has bounced"
# The HTML body of the email.
BODY_HTML = """<html>
<head></head>
<body>
<p>Email to %(bounceEmailAddressStr)s has bounced</p>
<p>Reason: %(bounceReasonStr)s</p>
<p>Complete details:%(jsonFormattedStr)s</p>
</body>
</html>""" % { "bounceEmailAddressStr": bounceEmailAddress, "bounceReasonStr": bounceReason, "jsonFormattedStr": json_formatted_str_text}
sendSESEmail (subject, BODY_TEXT, BODY_HTML)
else:
print("Email is Complaint")
# The email body for recipients with non-HTML email clients.
BODY_TEXT = "SES: Complaint email notification" +"\r\n"+json_formatted_str_text
complaintEmailAddress = bouceComplaintMsg['complaint']['complainedRecipients'][0]['emailAddress']
complaintReason = bouceComplaintMsg['complaint']['complaintFeedbackType']
print("complaintEmailAddress == "+complaintEmailAddress)
print("complaintReason == "+complaintReason)
subject = "SES Alert: Email "+complaintEmailAddress+" has raised a Complaint"
# The HTML body of the email.
BODY_HTML = """<html>
<head></head>
<body>
<p>Email %(complaintEmailAddressStr)s has raised a Complaint</p>
<p>Reason: %(complaintReasonStr)s</p>
<p>Complete details:%(jsonFormattedStr)s</p>
</body>
</html>""" % { "complaintEmailAddressStr": complaintEmailAddress, "complaintReasonStr": complaintReason, "jsonFormattedStr": json_formatted_str_text}
sendSESEmail (subject, BODY_TEXT, BODY_HTML)
def sendSESEmail(SUBJECT, BODY_TEXT, BODY_HTML):
# Send the email.
try:
#Provide the contents of the email.
response = sesClient.send_email(
Destination={
'ToAddresses': [
toEmail,
],
'CcAddresses': [
ccEmail,
]
},
Message={
'Body': {
'Html': {
'Charset': CHARSET,
'Data': BODY_HTML,
},
'Text': {
'Charset': CHARSET,
'Data': BODY_TEXT,
},
},
'Subject': {
'Charset': CHARSET,
'Data': SUBJECT,
},
},
Source=fromEmail,
)
print("SES Email Sent.....")
# Display an error if something goes wrong.
except ClientError as e:
print("SES Email sent! Message ID:"+ e.response['Error']['Message'])
else:
print("SES Email sent! Message ID:" + response['MessageId'])
def pp_json(json_thing, sort=True, indents=4):
if type(json_thing) is str:
print("json is a str")
return (json.dumps(json.loads(json_thing), sort_keys=sort, indent=indents).replace(' ', ' ').replace('\n', '<br>'))
else:
return (json.dumps(json_thing, sort_keys=sort, indent=indents).replace(' ', ' ').replace('\n', '<br>'))
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print(event)
sendSESAlertEmail(event)
Step 4: Testing and Validation
Once configured, it's important to test the setup:
- Send test emails that will trigger bounce or complaint notifications.
- Verify that these notifications are received by SNS and correctly trigger the Lambda function.
Step 5: Monitoring and Adjustments
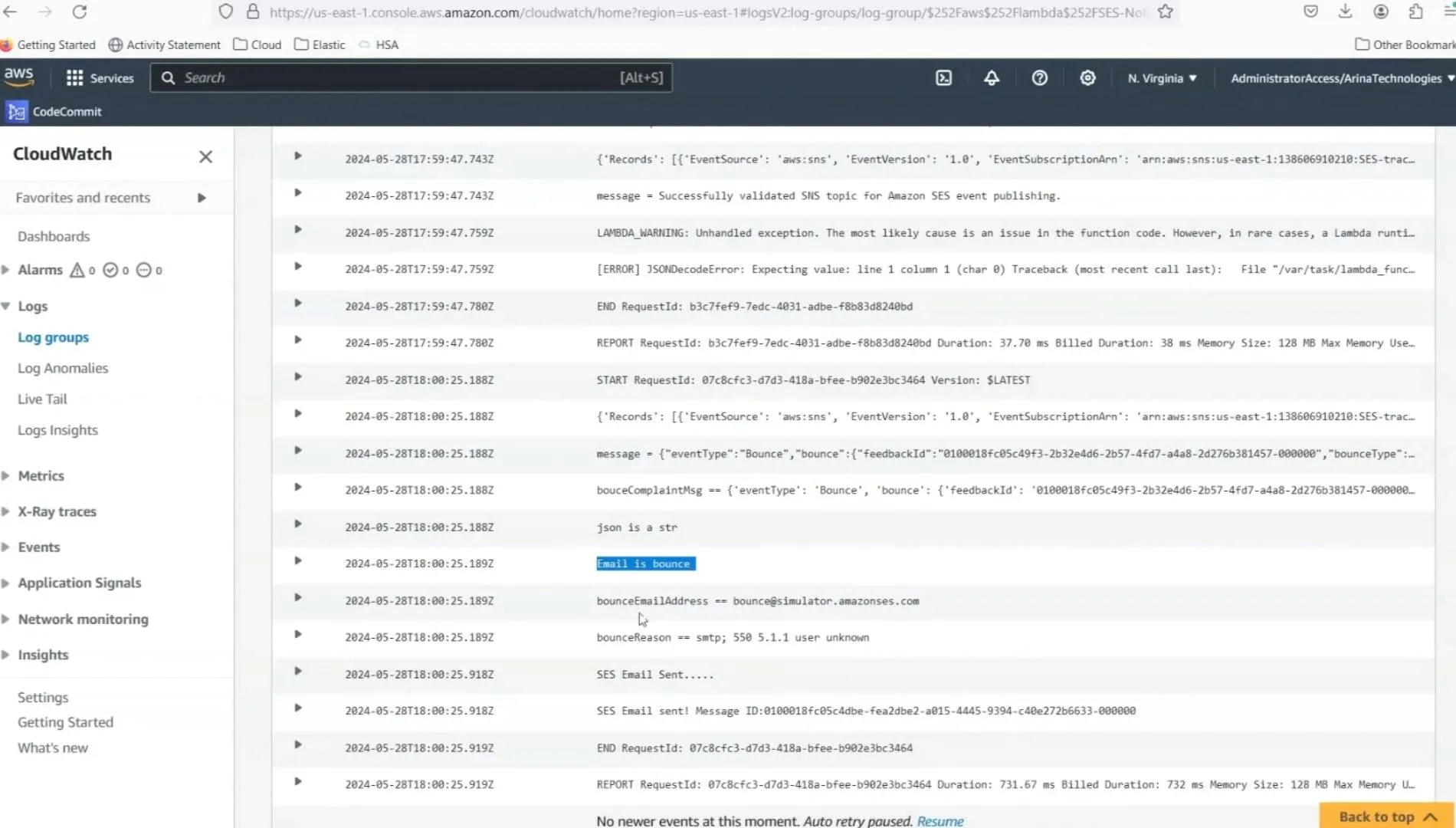
Regularly monitor the setup through AWS CloudWatch and adjust configurations as necessary to handle any new types of email issues or to refine the process.
Advanced Considerations
Consider exploring more advanced configurations such as:
- Setting up dedicated Lambda functions for different types of notifications.
- Using AWS KMS (Key Management Service) for encrypting the messages that flow between your services for added security.
Please refer our Newsletter where we provide solutions to creating customer marketing newsletter.
Conclusion
This setup not only ensures that your organization responds swiftly to critical email events but also helps in maintaining a healthy email environment conducive to effective communication. Automating the handling of email bounces and complaints with AWS SES, SNS, and Lambda represents a proactive approach to infrastructure management, crucial for businesses scaling their operations.