Building a Center of Excellence: Non-Functional Requirements, Decision Framework, and Key Artifacts
Please read Center of Excellence on what is a Center of Excellence, how to set it up and the different organization setup.
Key Artifacts for CCoE
To ensure the success of a CCoE, specific artifacts are essential. These artifacts not only establish governance but also provide a structured roadmap for cloud adoption and maintenance. As organizations increasingly migrate to cloud environments, establishing a Cloud Center of Excellence (CCoE) is paramount for ensuring effective governance, decision-making, and operational efficiency. This article delves into the key artifacts and governance strategies essential for setting up and managing a successful CCoE.
1. Cloud Decision Framework
The decision framework ensures that applications transitioning to the cloud adhere to compliance, legal, and business requirements. Here's how to approach it:
- Evaluate compliance requirements: Ensure the cloud environment meets legal and industry-specific standards.
- Customer and legal validation: Confirm customer approval and legal clearance for data storage on the cloud.
- Business case preparation: Develop a business case detailing the operational and financial benefits of the transition.
A robust cloud decision framework ensures that no critical factors are overlooked during migration.
2. Non-Functional Requirements (NFRs)
Non-functional requirements or NFRs are critical for defining the scalability, performance, and reliability of applications in the cloud. NFRs should include:
- Performance metrics: Define response times, latency, and throughput.
- Scalability: Plan for traffic surges during events like Black Friday or other peak times.
- Availability: Set clear Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTO).
- Security: Implement robust data protection measures and comply with data residency regulations.
- Resiliency: Prepare for disaster recovery scenarios with effective Recovery Point Objectives (RPO).
- Observability: Establish monitoring, logging, and alerting systems.
Organizations can use these NFRs to ensure their cloud applications meet user and business expectations effectively.
Availability Percentage to Time (Seconds, Minutes, Hours)
Availability is one of the most critical aspects of any cloud infrastructure. The table above provides a clear breakdown of availability percentages and the corresponding downtime:
- 99% Availability ("Two Nines"): 3.65 days of annual downtime.
- 99.9% Availability ("Three Nines"): 8.77 hours of annual downtime.
- 99.99% Availability ("Four Nines"): 52.60 minutes of annual downtime.
- 99.999% Availability ("Five Nines"): 5.26 minutes of annual downtime.
Following diagram provides further mapping of availability Percentage to time.
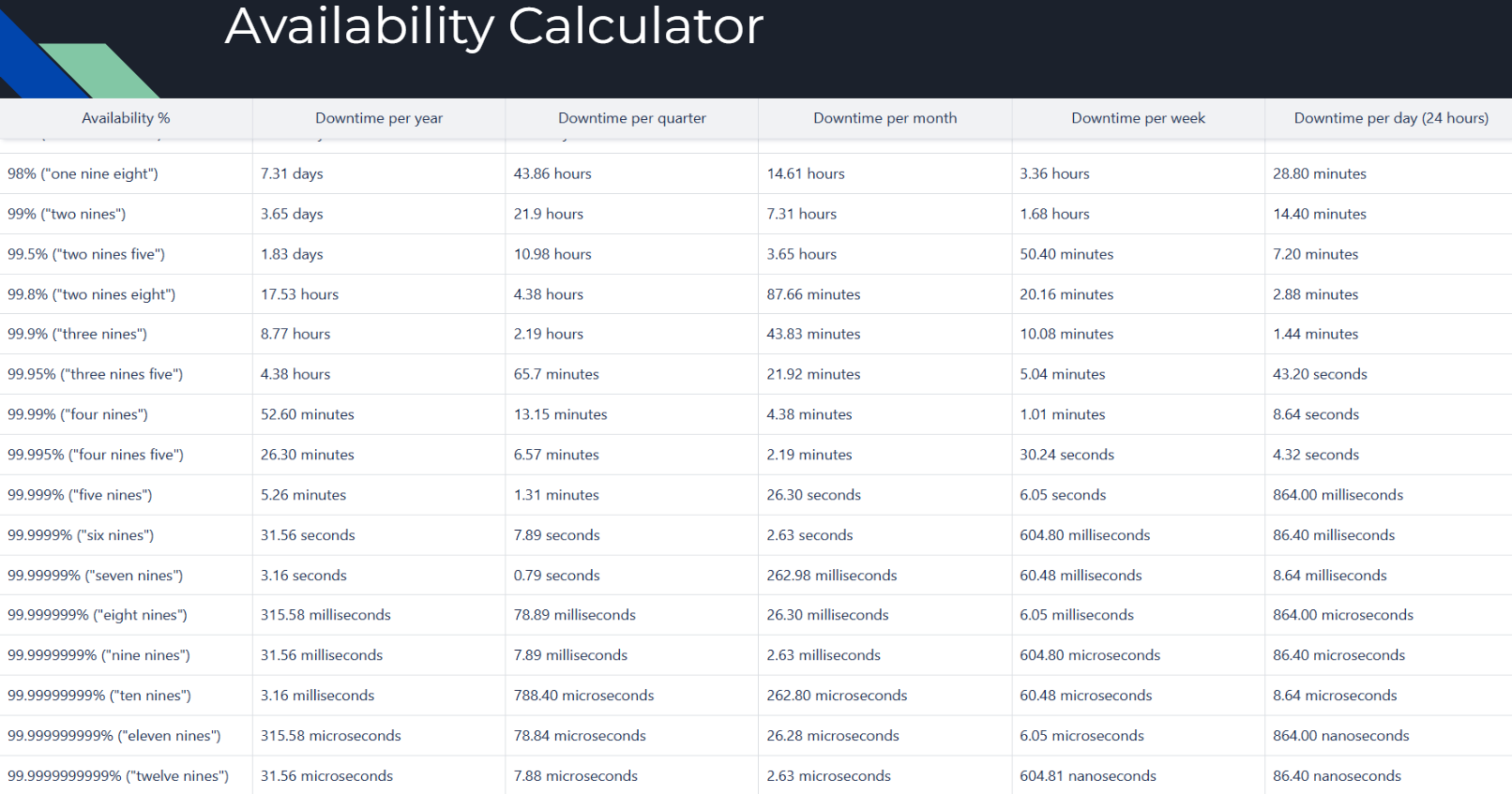
Key Insight: Striving for higher availability percentages often involves more complexity and cost. Businesses should align their availability goals with operational requirements and budget constraints.
Operations Template
The operations template ensures readiness for smooth application deployment and maintenance. Key areas to consider:
- OS and Database Version Support: Ensuring compatibility and updated versions (e.g., SQL Server Standard 2019).
- Disaster Recovery (DR) Testing: Regularly scheduled DR testing is crucial.
- Observability: Tools like Grafana provide essential logging and monitoring capabilities.
- Alerting and Monitoring Integration: Platforms such as Ops Genie help automate notifications.
- Planned Downtime and Backup Schedules: Clearly defined schedules to minimize disruptions.

Pro Tip: Invest in ITSM (IT Service Management) tools to streamline these operations.
Data Template
Efficient data processing is a cornerstone of cloud operations. The data template above outlines critical considerations:
- Batch vs. Real-Time Processing: Determine whether batch or real-time data handling aligns with your business use case.
- Data Size and Growth: Plan for storage based on expected growth (e.g., 1TB/year for streaming data).
- Processing Time: Define clear SLAs for response, query, and reporting times (e.g., 10 seconds for streaming).
- Exception Handling: Implement retries and error reporting mechanisms to handle processing failures.
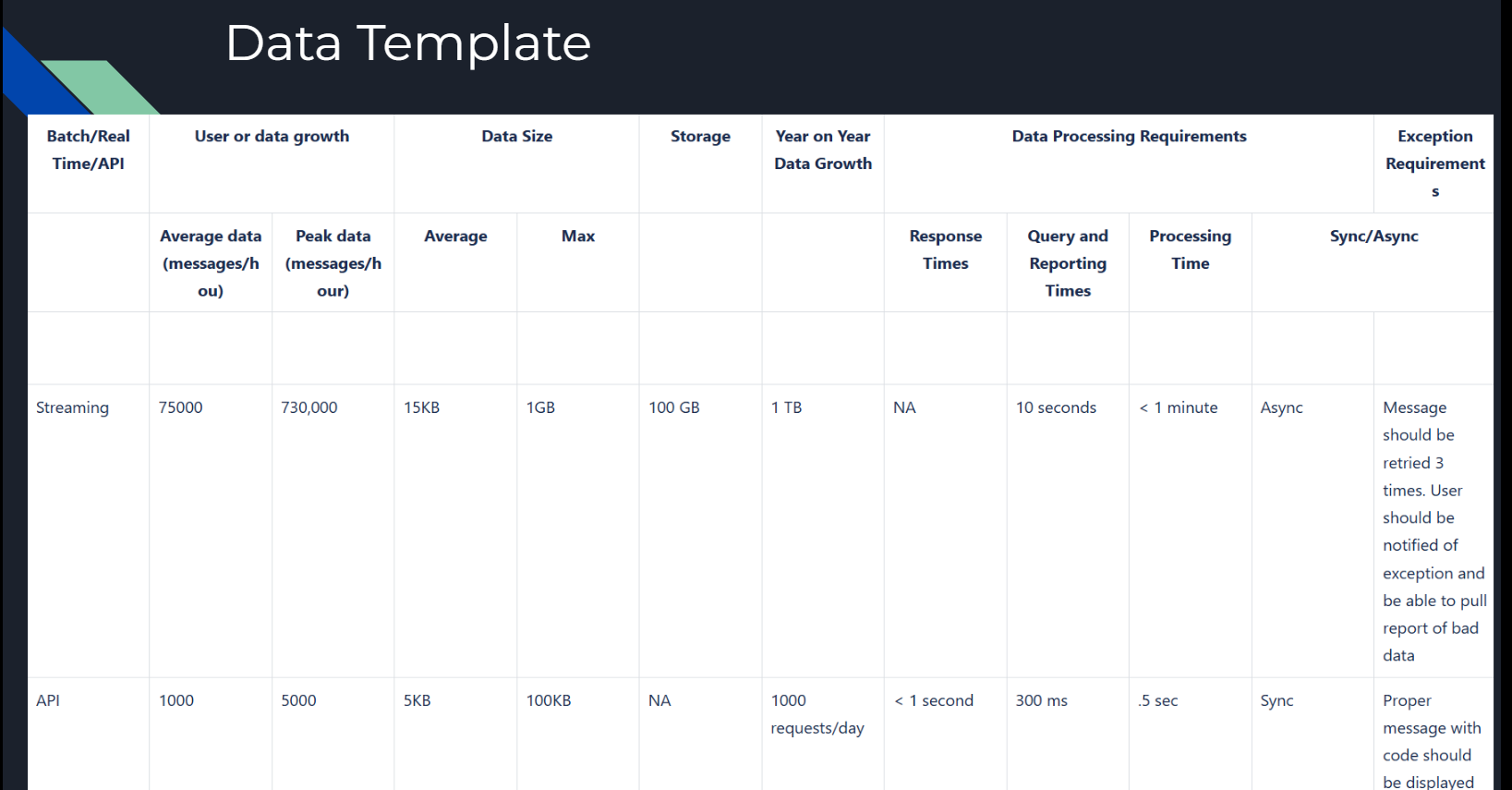
Best Practice: Opt for real-time processing wherever possible to enhance responsiveness and scalability.
Business Template
The business template focuses on aligning technical requirements with business goals. Key fields include:
- Data Classification: Categorize data as internal, public, confidential, or restricted.
- Application Criticality: Prioritize applications based on their impact on business operations.
- Compliance and Security Requirements: Ensure adherence to regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI.
- Availability and Recovery Objectives: Set realistic RPO (Recovery Point Objective) and RTO (Recovery Time Objective) metrics.
- Data Retention Policies: Define how long data needs to be stored and maintained.
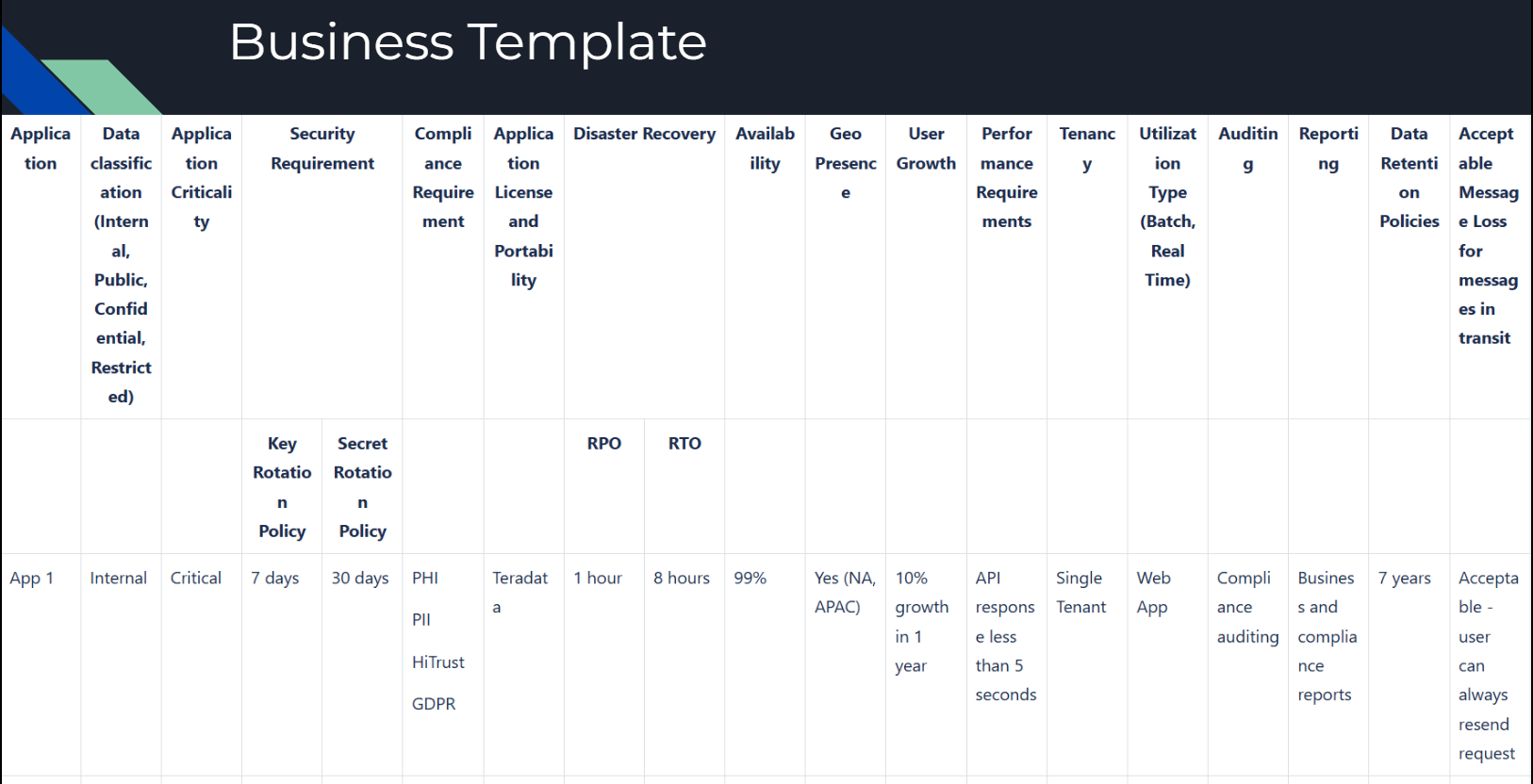
Actionable Insight: Collaboration between technical teams and business stakeholders is essential to define and meet these requirements.
Infrastructure Template
This template helps define the physical and virtual setup:
- Environment: E.g., development or production.
- Hosting Location: On-premises or cloud-based.
- Hardware Requirements: CPU, memory, and storage capacity.
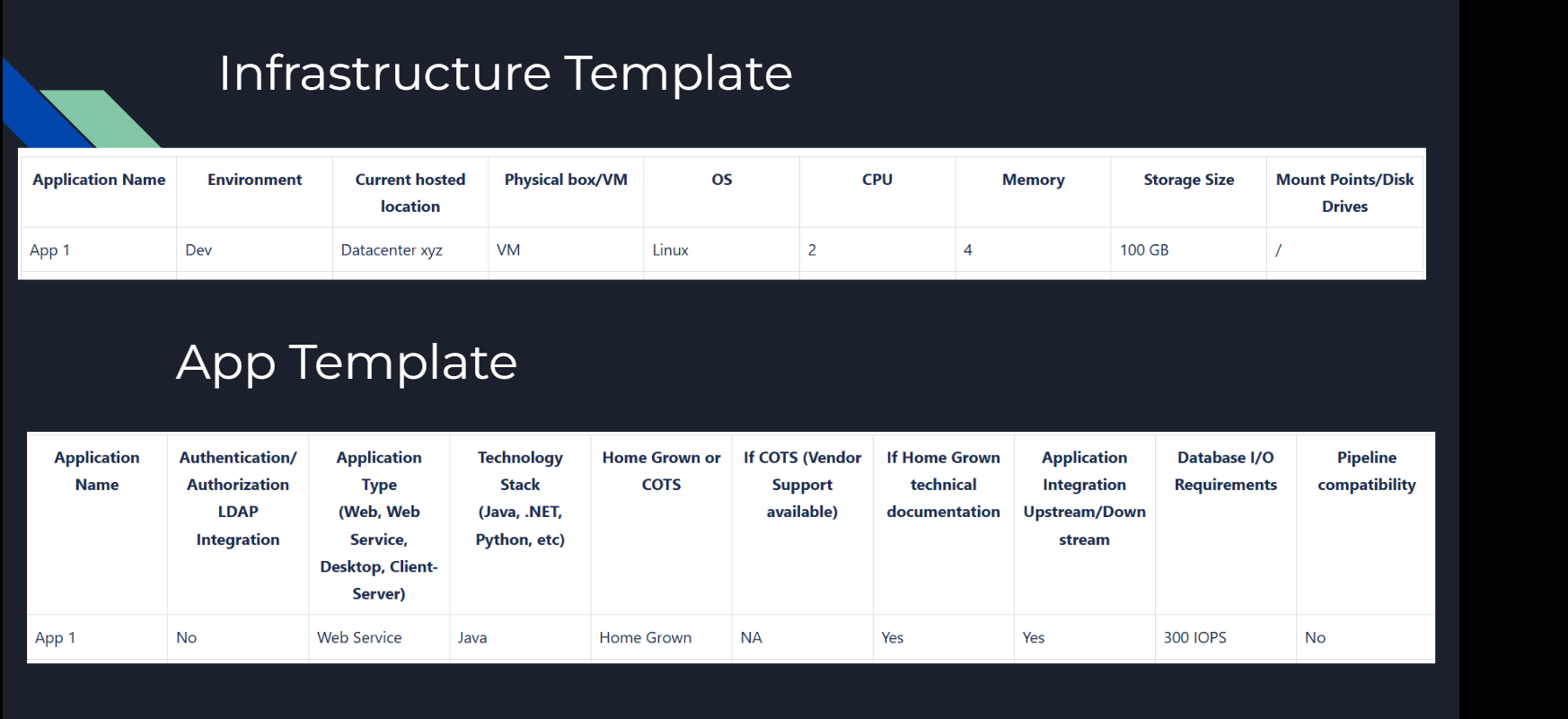
Application Template
Key application details:
- Authentication/Authorization: Integration with LDAP or OAuth.
- Technology Stack: Define the programming language and framework.
- Pipeline Compatibility: Ensure smooth CI/CD pipeline integration.
Recommendation: Use these templates during the planning phase to streamline cloud migration and infrastructure setup.
3. Architecture Diagrams
Detailed architecture diagrams are crucial for:
- Illustrating traffic flows and component interactions.
- Documenting ingress and egress points.
- Representing hybrid or multi-cloud environments.
- Standardizing visual representations for clear communication.
There are lot of architecture templates available that can show not only to depict the resources but only the network diagram. These diagrams will facilitate clarity among teams and ensure compliance with governance standards.
4. Business Case and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Cloud adoption requires a well-documented business case and financial analysis:
- Five-year outlook: Compare on-premises costs with cloud hosting to project savings and ROI.
- CapEx vs. OpEx: Highlight the financial benefits of shifting from capital expenditure to operational expenditure.
- Cloud calculators: Use tools like AWS or Azure cost calculators to provide accurate cost projections.
A comprehensive TCO analysis helps align cloud adoption with organizational financial strategies.
5. Milestones and Timelines
Clear milestones and timelines are essential for seamless cloud adoption. Ensure that:
- Dependencies are identified: Coordinate with operations, security, and QA teams.
- Agile methodology is followed: Use Sprint or Kanban models for efficient project management.
Detailed timelines prevent bottlenecks and ensure timely execution of tasks.
Conclusion
Establishing a Cloud Center of Excellence involves meticulous planning, robust governance frameworks, and continuous monitoring. By focusing on key artifacts such as decision frameworks, NFRs, architecture diagrams, and cost analyses, organizations can ensure a smooth transition to the cloud.
Ready to take your cloud infrastructure to the next level?
Contact Us to discuss how we can help your organization in Staffing, Consulting, Web Development
Subscribe to our newsletter for insights on cloud computing, tips, and the latest trends in technology.